The versatile and sustainable material known as Ethylene Terephthalate (ETPU) has gained significant traction in recent years due to its exceptional properties such as strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance. However, one of the key considerations when integrating ETPU into existing recycling processes is finding suitable materials for its recycling.
ETPU machines are equipped with advanced technology that enables them to process a wide range of materials including plastics, metals, glass, paper, and more. This makes ETPU an ideal choice for recycling applications where it can contribute significantly to environmental sustainability and resource recovery efforts.
As per current research, there are several recyclable materials that can be effectively recycled using ETPU machines. These include:
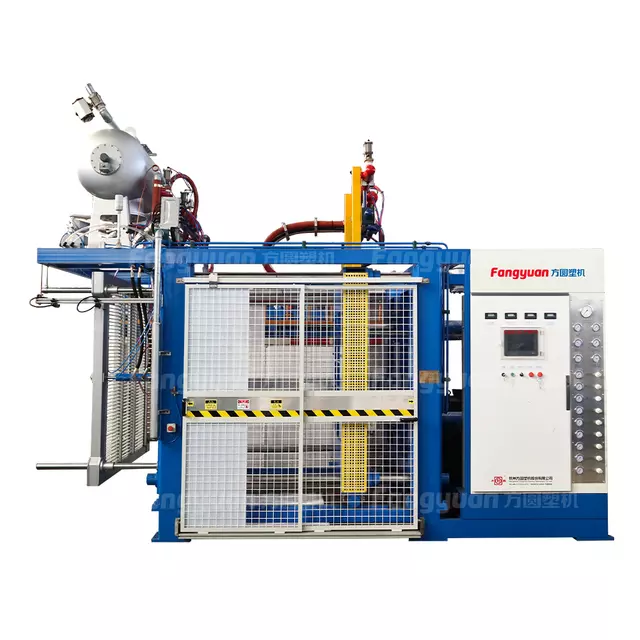

Plastics ETPU machines can process various types of plastic waste, including but not limited to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), and others.
Metals In certain cases, ETPU machines have been designed to recycle certain metals such as aluminum and steel, though these capabilities vary depending on the specific machine model.
Glass While ETPU machines may not directly recycle glass due to the nature of the material's composition, they can sometimes process broken glass through a separate process, making use of their ability to withstand impact.
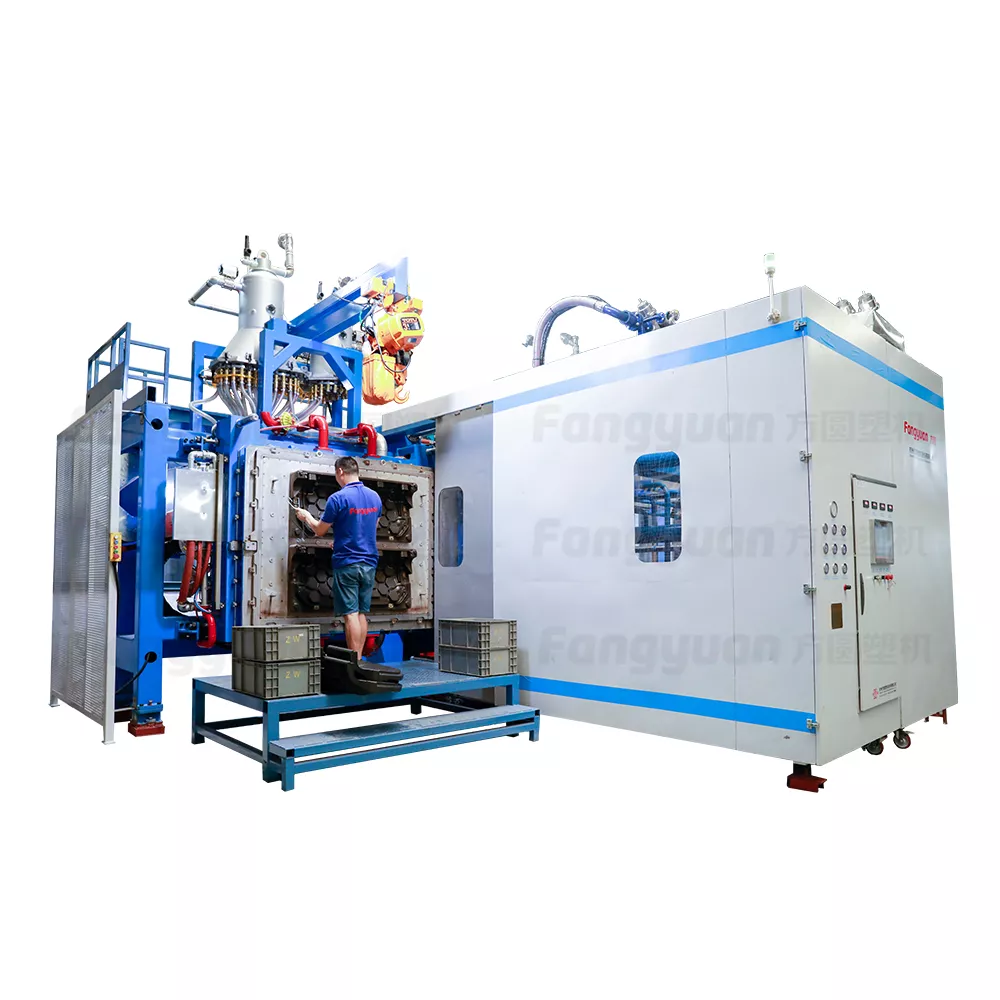

Paper The processing of paper involves stripping away noncore components like cardboard and metal foil, which are then separated from the core fibers, before being fed back into the ETPU machine for recycling.

In addition to this, ETPU machines also offer opportunities for postconsumer recycling of textiles, which can be processed by removing the inner lining and other removable parts while maintaining the structure of the fabric.
Overall, the versatility of ETPU makes it an attractive option for recycling programs worldwide. With advancements in technology and increased interest in sustainable practices, ETPU machines continue to play a crucial role in transforming the way we manage our waste streams, ensuring a more circular economy for generations to come.






















 QQ
QQ